Five Definitions of Gravitation : Gravitation, the fundamental force of attraction between objects with mass, is a concept that has captivated human curiosity for centuries.
From the groundbreaking insights of Sir Isaac Newton to the revolutionary theories of Albert Einstein, our understanding of gravitation has evolved, revealing its profound role in shaping the cosmos.
In this presentation, we embark on a journey through five diverse definitions of gravitation, delving into the classical and modern interpretations that help us comprehend the mysteries of our universe.
Join us as we explore the essence of gravitation, from Newton’s gravitational pull to Einstein’s spacetime curvature, and discover how this force governs the movements of celestial bodies and influences our daily lives.”
Here are five definitions of gravitation, each described in five different ways | universal law of gravitation
Definition 1: Newtonian Perspective
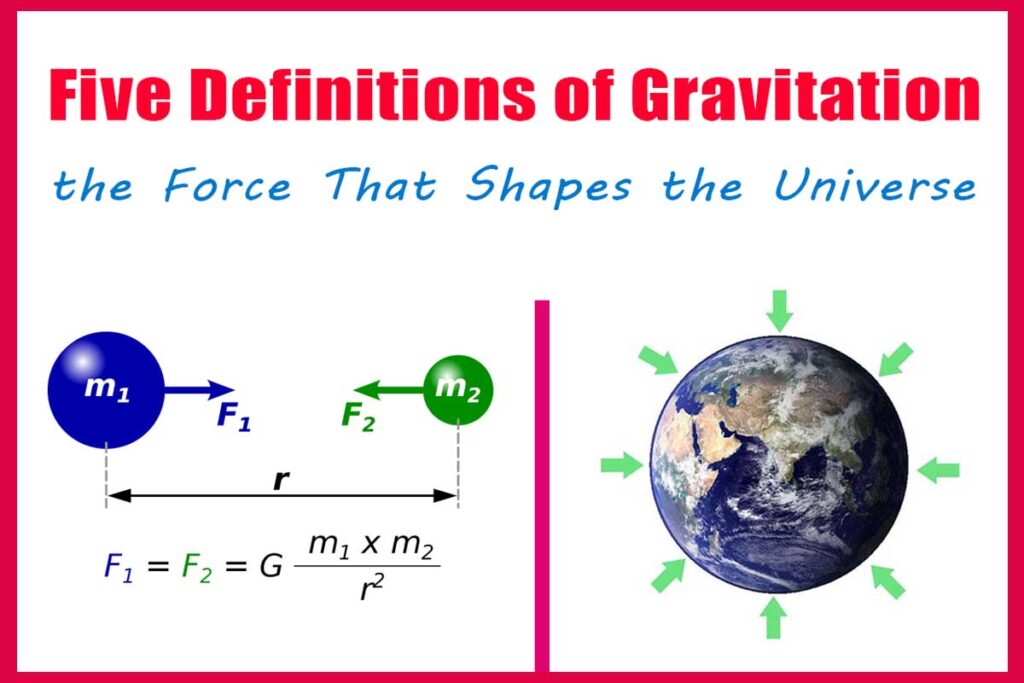
Gravitation is the force of attraction between two objects with mass.
It is the mutual pull that massive objects exert on each other.
This force is directly proportional to the product of their masses.
It is inversely proportional to the square of the distance between them.
Gravitation follows Newton’s law of universal gravitation.
Definition 2: Einstein’s Space-Time Concept
Gravitation is the warping or curvature of space-time caused by mass and energy.
Massive objects create dimples or depressions in the fabric of space-time.
Other objects move along curved paths within this distorted space-time.
The appearance of attraction results from the bending of these paths.
Gravitation is explained by Einstein’s general theory of relativity.
Definition 3: Gravitational Field Interpretation
Gravitation is a gravitational field surrounding massive objects.
Objects with mass experience a force when placed within this field.
The strength of the field depends on the mass of the object creating it.
The field extends infinitely outward from the massive object.
The force experienced by an object in the field is proportional to its mass.
Definition 4: Gravitational Acceleration
Gravitational acceleration is the rate at which objects fall due to gravity.
It is the acceleration experienced by objects in a gravitational field.
On Earth, this acceleration is approximately 9.81 meters per second squared (m/s²).
Gravitational acceleration is responsible for the weight of objects on a planet.
It varies from one celestial body to another depending on their masses.
Definition 5: Celestial Mechanics Perspective
Gravitation governs the interactions between celestial bodies.
It determines the orbits of planets around the Sun.
Moons are held in orbit around planets by the force of gravitation.
Gravitational interactions are responsible for tides on Earth.
The entire structure and motion of the universe are influenced by gravitation.
state the universal law of gravitation