Chemical Reactions And Equations- Use Your Brain Power : Maharashtra State Board Science-1-Chapter-3- Chemical Reactions And Equations- Use Your Brain Power | Fascinating

Use your brain power!

1) What is the number of reactants in each of the above reactions?
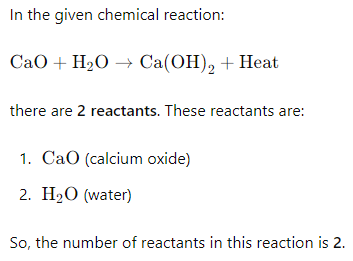
2) What is the number of molecules of reactants taking part in the above reactions ?
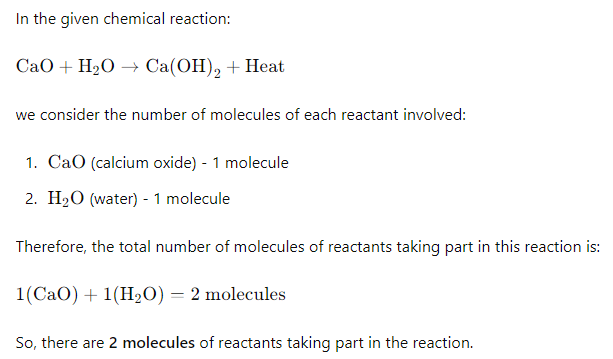
3) How many products are formed in each of the above reactions?

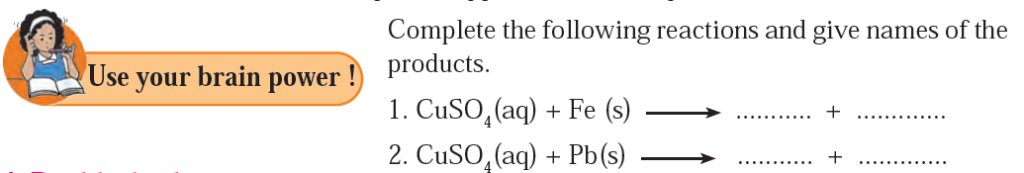
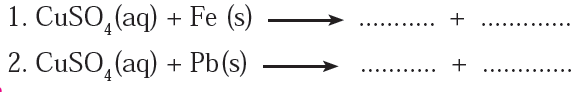
4) Complete the following reactions and give names of the products.


5) What is the difference in the process of dissolution and a chemical reaction ?

6) Does a new substance form when a solute dissolves in a solvent ?
In summary:
- Dissolution is a physical process with no new chemical substances formed.
- Chemical reaction involves the formation of new substances with different chemical properties.
- No new substance is formed when a solute dissolves in a solvent; the solute and solvent retain their original chemical identities.
7) Which is the oxidant used for purification of drinking water?
- Chlorine (Cl2):
- Form: Chlorine can be added to water in the form of chlorine gas (Cl2), sodium hypochlorite (NaOCl), or calcium hypochlorite (Ca(OCl)2).
- Function: It acts as a strong oxidizing agent, effectively killing bacteria, viruses, and other pathogens in the water.
- Mechanism: Chlorine works by breaking down the cell walls of microorganisms and disrupting their metabolism, leading to their destruction.
- Other Oxidants:
- Ozone (O3): Another powerful oxidant sometimes used for water purification. It is more effective than chlorine at disinfecting water and leaves no residual taste or odor, but it is more expensive and must be generated on-site.
- Chlorine Dioxide (ClO2): Used for specific applications due to its strong oxidizing properties. It is effective against a wide range of pathogens, including those resistant to chlorine.
- Potassium Permanganate (KMnO4): Occasionally used for specific water treatment purposes, such as controlling taste and odor or removing iron and manganese.
Why Chlorine is Preferred:
- Cost-Effective: Chlorine is relatively inexpensive compared to other oxidants.
- Residual Protection: Chlorine provides a residual disinfecting effect, meaning it continues to protect the water from microbial contamination as it travels through the distribution system.
- Proven Efficacy: It has been used for decades and has a well-documented record of effectively reducing waterborne diseases.
In summary, while various oxidants can be used for water purification, chlorine is the most commonly used due to its cost-effectiveness, residual protection, and proven efficacy.
8) Why is potassium permanganate used during cleaning water tanks?
Potassium permanganate (KMnO4 is used during the cleaning of water tanks for several reasons:
Oxidizing Properties
- Strong Oxidizing Agent: Potassium permanganate is a powerful oxidizing agent, which allows it to effectively oxidize and break down organic matter, including bacteria, algae, and other contaminants in the water tank.
Disinfection
- Microbial Control: It helps in controlling microbial growth by oxidizing cell walls and cellular components of bacteria, algae, and fungi, thereby killing or inhibiting their growth.
Removal of Organic Contaminants
- Oxidation of Organic Matter: KMnO4 can oxidize and remove organic contaminants, such as biofilm and organic sediments, which can accumulate in water tanks over time.
Iron and Manganese Removal
- Oxidation of Iron and Manganese: It oxidizes soluble iron (Fe2+ and manganese (Mn2+ to their insoluble forms (Fe3+ and MnO2, which can then be filtered out. This is particularly useful in areas where water contains high levels of these metals.
Odor Control
- Reduction of Odors: The oxidation of organic compounds and contaminants helps to reduce unpleasant odors that may develop in water storage tanks.
Safe and Effective
- Safe for Use: When used in appropriate concentrations, potassium permanganate is safe and effective for cleaning and disinfecting water tanks. It does not produce harmful byproducts when used properly.
Visual Indicator
- Visual Indicator: The distinct purple color of potassium permanganate solutions provides a visual indicator, making it easier to ensure thorough mixing and coverage during the cleaning process.
Application Process
- Preparation: A dilute solution of potassium permanganate is prepared, typically by dissolving a small amount of KMnO4 in water.
- Application: The solution is applied to the water tank surfaces and allowed to sit for a specified period, ensuring contact with all surfaces.
- Rinsing: After the oxidation and disinfection process, the tank is thoroughly rinsed to remove any residual potassium permanganate and oxidized contaminants.
In summary, potassium permanganate is used during the cleaning of water tanks due to its strong oxidizing properties, effectiveness in controlling microbial growth, ability to remove organic and inorganic contaminants, and its role in reducing odors, all while being safe and providing a visual indicator for proper application.